Middle ear implants

Middle ear implants are suitable for use by people with a mild-moderate mixed or conductive hearing loss or a sensorineural hearing loss.
It is a more recent form of hearing implant, offering an alternative to conventional hearing aids. An audiologist may consider this device for those who suffer from different symptoms, such as:
- earmould allergies
- skin problems in their ears
- outer ear infections
- narrow, collapsed or closed ear canals,
- malformed ears.
For those with mixed or conductive hearing losses, this implant is an alternative to a bone anchored hearing aid.
Additionally, it is a solution if a person experiences any of the above ear problems, may have healing issues, or dexterity problems. It can also be beneficial to those who might find difficulty in keeping a bone anchored hearing aid clean.
Image: Courtesy of MED-EL
How does a middle ear implant work?
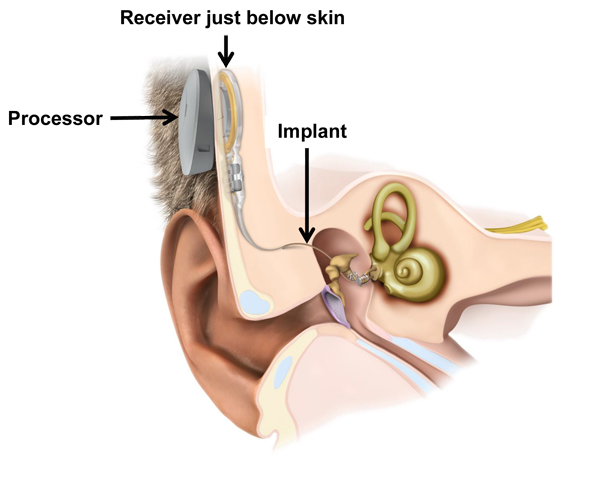
There are two parts to this device: an external part (the ‘processor’) and the surgically-implanted internal part.
The processor transmits sound to the internal part of the hearing implant which consists of a receiver just below the skin.
The receiver, together with the implant, picks up sound from the processor, that is attached to one of the bones in the middle ear or to the membrane window of the cochlea.
The implant works by directly moving the bones of the middle ear, or by vibrating the membrane window of the cochlea.
In either case, this device is designed to amplify sounds by adding extra movement into the natural hearing pathway. The middle ear implant relies on a working cochlea and hearing nerve.
Image: Courtesy of MED-EL
Who is considered for one?
A middle ear implant is an option when a conventional hearing aid is not appropriate, or does not give effective benefit.
Request an information pack
Find out more about the range of personalised services we offer. Fill out our webform to receive an information pack.
What can I expect from a middle ear implant?
These devices offer amplification without an earmould in the ear. This makes them more comfortable if you experience discomfort or infections in your ear. Some people also report that they have a more natural sound than conventional hearing aids for the same reason. They do not restore your hearing to normal, but can make managing in everyday situations easier.
The audio processor of a middle ear system can connect to external devices via Bluetooth or telecoil. This enables the signal from a mobile device, MP3 player, FM system or assistive listening device to transmit wirelessly to the audio processor with no loss of sound quality.
How a middle ear implant works video
Courtesy of MED-EL
Further information visit MED-EL’s website.
Webpage updated: April 2024